Call Agent:+91-77018 79973
Send Email:
[email protected]
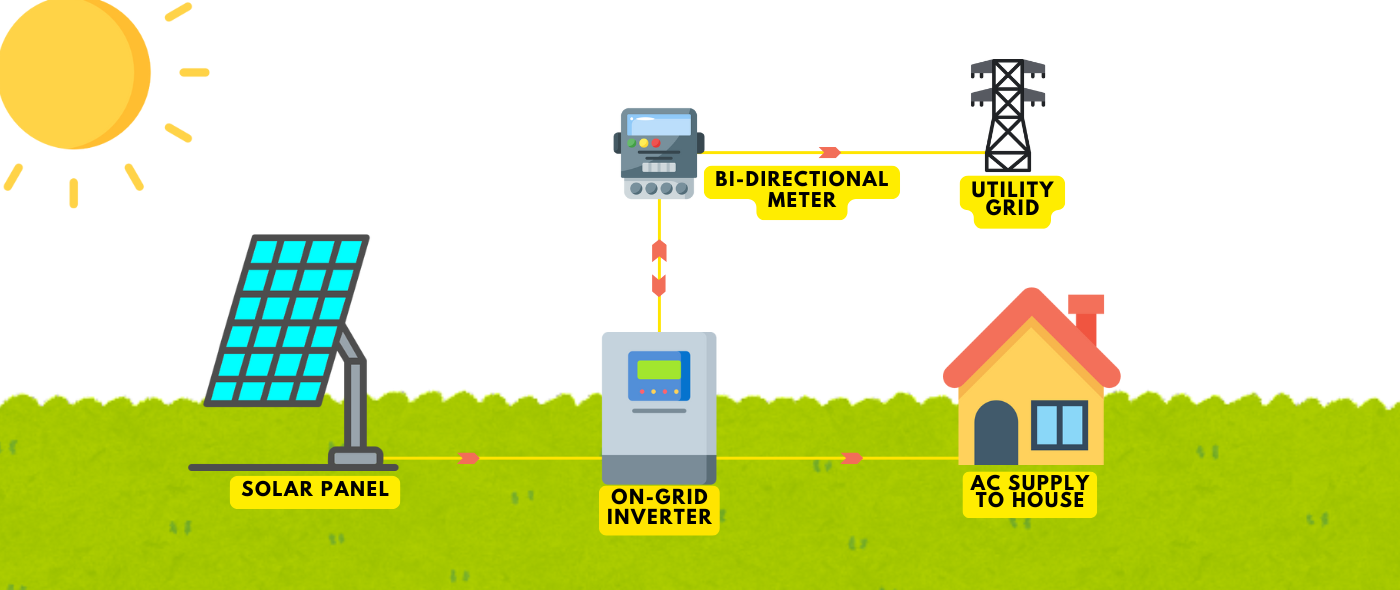
Installation and Maintenance of Solar Panels
Practical renewable energy technology thatreduces costs and helps the environment

Get in touch
Office 04, Building 16, Bharat Nagar, New Friends Colony, New Delhi-110025